Data Serialization and Deserialization: A Beginner's Guide
- 10 Oct, 2025
In this post, we’ll talk about the essentials of data serialization and deserialization, so you can quickly understand how they work, common formats, and why they’re so important in modern computing. Let’s start!
Introduction to Data Serialization
Data Serialization is the process of converting complex data structures or objects into a format that can be easily stored or transmitted. This serialized data can later be reconstructed into its original form through a process called Deserialization.
What is Data Serialization?
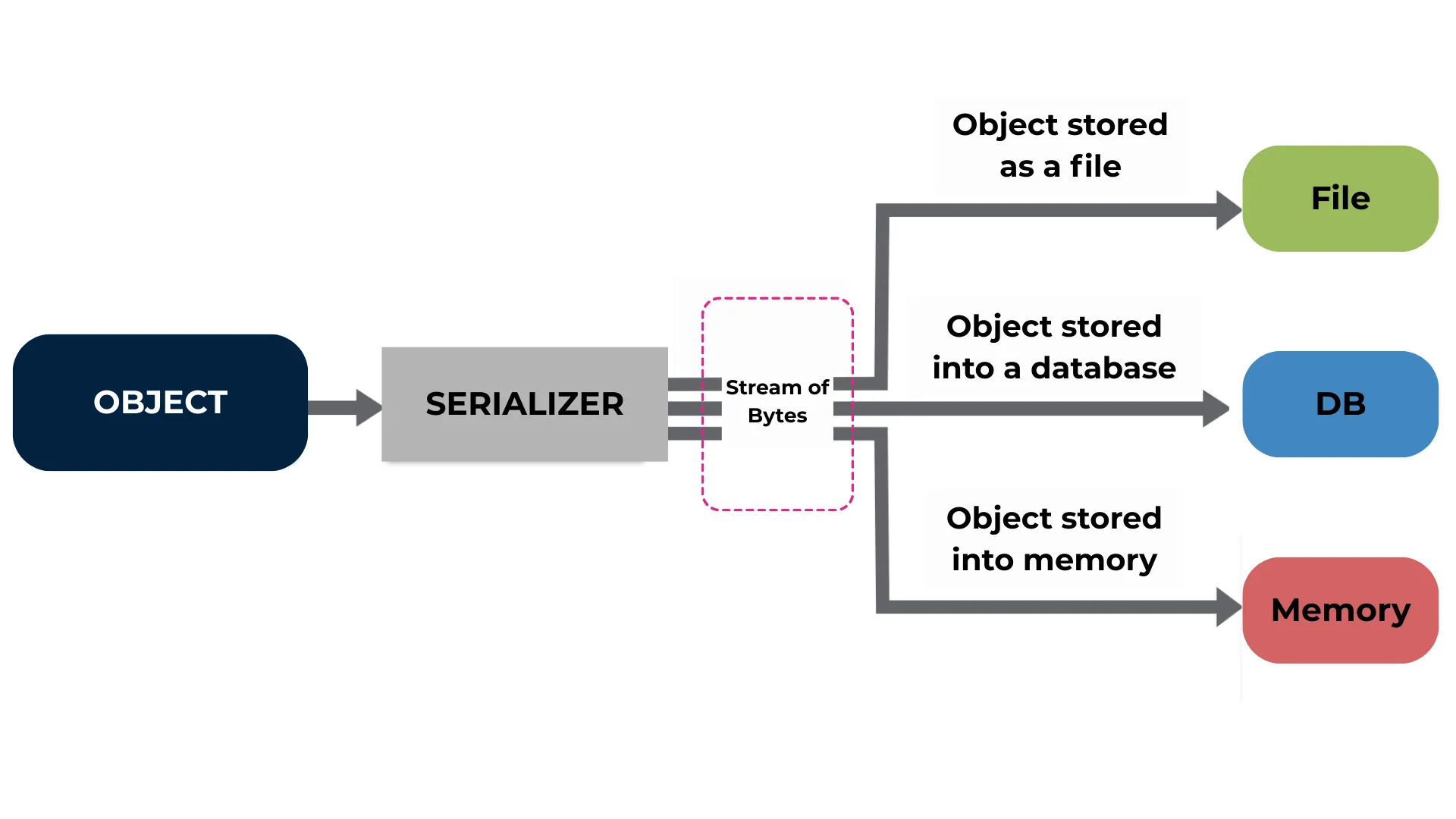
Data serialization converts data objects into a byte stream (a sequence of bytes that represents the data). These byte streams can be stored on disk, transferred over networks, or processed by other systems. This conversion keeps the data’s structure intact while making it portable across different systems or platforms.
The reverse process, Deserialization, takes the byte stream and reconstructs it back into the original object form.
Serialized data is platform-independent and is commonly stored in formats such as:
- JSON: Human-readable and widely used in web applications.
- XML: Common for document storage and data exchange.
- Binary: Raw data format typically used for internal storage.
Each of these formats ensures data can be stored, transmitted, and reconstructed consistently across various environments, regardless of hardware or operating systems.
How Does Data Serialization Work?
-
Serialization Process: Data objects are passed through a serializer (a component or algorithm that converts them into a byte stream). This byte stream is then stored or transmitted.
Example: A
Personobject in your program (with fields likename,age, etc.) can be serialized into a JSON string, which can be saved to a file or sent over a network. -
Deserialization: When needed, the byte stream is received and converted back into the original object format that your program can use.
Example: The JSON string received over the network is deserialized back into a
Personobject with all its original attributes (name,age, etc.).
Applications of Data Serialization
1. Persisting Data
Serialization allows you to save program data into files in either human-readable formats like JSON, XML, or CSV, or in compact binary forms for efficiency.
Example: In Java, the Serializable interface lets you serialize objects into binary format and save them to a file.
2. Storing Data in Databases
Serialized data can be stored directly in databases as byte streams.
Example: Saving a serialized Person object as a BLOB (Binary Large Object) in a relational database.
3. Transmitting Data
Serialization enables efficient data transfer between systems, such as client-server communication.
Example: A web service serializes user data (like login info) into JSON, sends it over HTTP, and the server deserializes it for processing.
4. Remote Method Invocation (RMI)
Serialized objects can be passed as parameters in remote function calls, allowing data transmission across network boundaries.
Example: In Java RMI, objects are serialized and sent to a remote server as if they were local.
Benefits of Data Serialization
-
Data Persistence: Save the state of an object and retrieve it later—ideal for sharing data across sessions or systems.
-
Storage Efficiency: Serialized data usually takes up less space than in-memory data, making it great for storage or transmission.
-
Interoperability: Share data across different languages and platforms (e.g., serialize in Python and deserialize in Java).
-
Faster Data Transfer: Simplifies transmitting data over networks, improving communication speed between systems.
-
Cross-Platform Communication: Serialized data works across different operating systems and hardware architectures.
Why Is Data Serialization Important for Distributed Systems?
In distributed systems, data is spread across multiple machines or clusters. Serialization enables these systems to communicate and share data efficiently. Some use cases include:
- Adding key-value objects to distributed maps.
- Sending messages to queues or topics in messaging systems.
- Storing and retrieving objects from distributed databases.
Serialization ensures data remains consistent and portable no matter where it lives or moves within the system.
Use Cases of Data Serialization
-
Data Storage: Serialize complex objects for storage in files, databases, or cloud services, using formats like JSON, XML, or binary.
-
Communication Between Systems: Web apps and microservices often serialize data for exchange. For example, REST APIs commonly use JSON.
-
Distributed Computing: Distributed systems pass objects between nodes or services using serialization to maintain consistency.
Final Thoughts
Data serialization is a fundamental concept in modern computing, especially when working with distributed systems, large-scale data storage, or network communication.
Understanding serialization helps you build efficient and scalable applications and ensures your data stays portable, secure, and easy to work with across platforms and programming languages.
Want to dive deeper? Check out these related topics: