Add Swagger UI to Nodejs Express REST API: Simple Setup Guide
- 19 Dec, 2025
Efficient QA and front-end integration depend on a strong API documentation. For developers working with nodejs. In this guide, we’ll integrate Swagger, one of the most popular documentation tools into a nodejs + express project using swagger-ui-express and swagger-autogen so that both your team and your testers can interact with your API smoothly. Let’s start!
1. Install Dependencies
Run the following command in your project directory:
npm install swagger-ui-express swagger-autogenThese dependencies will allow you to generate and serve Swagger documentation for your API.
2. Create the Swagger Configuration File
Add a file called swagger.js in your project root (or inside a /swagger folder if you prefer), then add the following:
// swagger.js
import swaggerAutogen from "swagger-autogen";
const doc = {
info: {
title: "Articles API",
description: "RESTful API for managing articles",
},
host: "localhost:8080", // Change for production
schemes: ["http"],
basePath: "/api", // If you don't want a route prefix just remove it
definitions: {
Article: {
title: "Example Article",
description: "This is an example description",
published: false,
},
},
};
const outputFile = "./swagger-output.json";
const endpointsFiles = ["./src/routes/article.routes.js"]; // Change for your routes file is
swaggerAutogen({ openapi: "3.0.0" })(outputFile, endpointsFiles, doc)
.then(() => {
console.log("✅ Swagger documentation generated!");
})
.catch((err) => console.error(err));Tip:
basePathensures all your routes include/apiif your router is mounted likeapp.use("/api", router). Otherwise, just leave it like/
3. Generate the Swagger JSON
Before running the generator, add this line to your package.json (if not already there):
"scripts": {
"swagger-autogen": "node swagger.js"
}Then run:
npm run swagger-autogenYou should see:
Swagger documentation generated!This creates the swagger-output.json file with all your API endpoints.
4. Serve Swagger UI in Your Server
If you haven’t installed swagger-ui-express, do so now:
npm install swagger-ui-expressThen, in your server.js file, add the following depending on your Node.js version:
Node < 22
import swaggerUi from "swagger-ui-express";
import { createRequire } from "module";
const require = createRequire(import.meta.url);
const swaggerFile = require("./swagger-output.json");
app.use("/api-docs", swaggerUi.serve, swaggerUi.setup(swaggerFile));Node 22+ (ESM with assert { type: “json” })
import swaggerUi from "swagger-ui-express";
import swaggerFile from "./swagger-output.json" assert { type: "json" };
app.use("/api-docs", swaggerUi.serve, swaggerUi.setup(swaggerFile));Note: For Node < 22, using
createRequireavoids syntax issues with JSON imports.
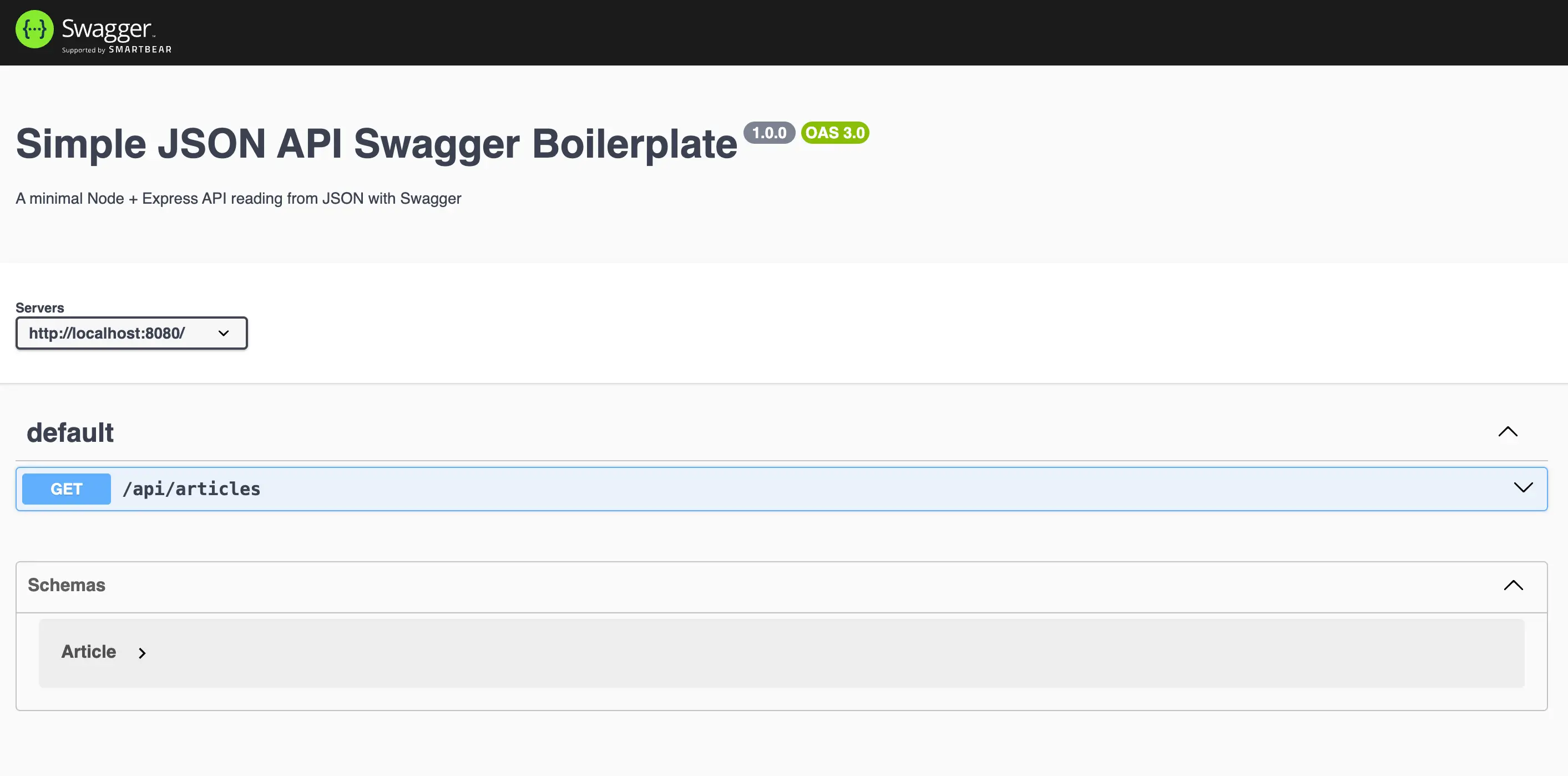
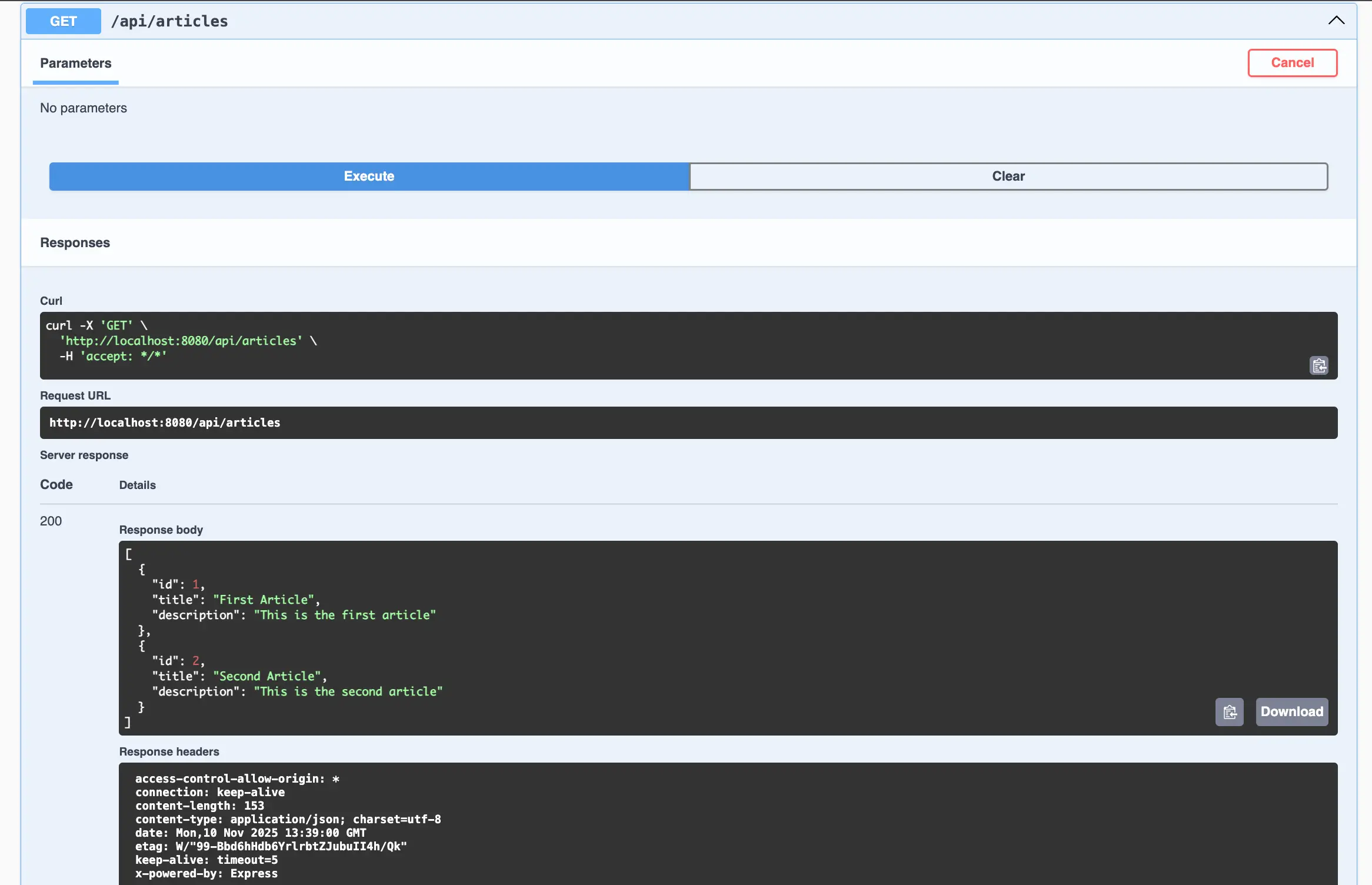
5. Test the Swagger UI
Start your server:
npm startThen open:
http://localhost:8080/api-docsYou should see all your API endpoints mapped correctly, including the /api prefix if you set basePath: "/api".
6. Update Swagger Docs Automatically
Whenever you modify or add routes, just re-run:
npm run swagger-autogenThis regenerates swagger-output.json with the new endpoints.
7. Optional Enhancements
- Add Request & Response Examples:
// In swagger.js definitions
definitions: {
Article: {
title: "My Article",
description: "Example content",
published: true,
},
},- Group endpoints by Tags
router.post("/article", async (req, res) => {
// #swagger.tags = ['Articles']
// #swagger.description = 'Create a new article'
});- Add parameter descriptions
Use Swagger comments above your route functions for body, query, or path params
swagger-autogenautomatically parses them.
Download the Boilerplate Project
👉 You can download the full working example from the GitHub Repo
Happy learning and thank you for reading!